News Release
Gross Domestic Product, 4th Quarter and Year 2024 (Advance Estimate)
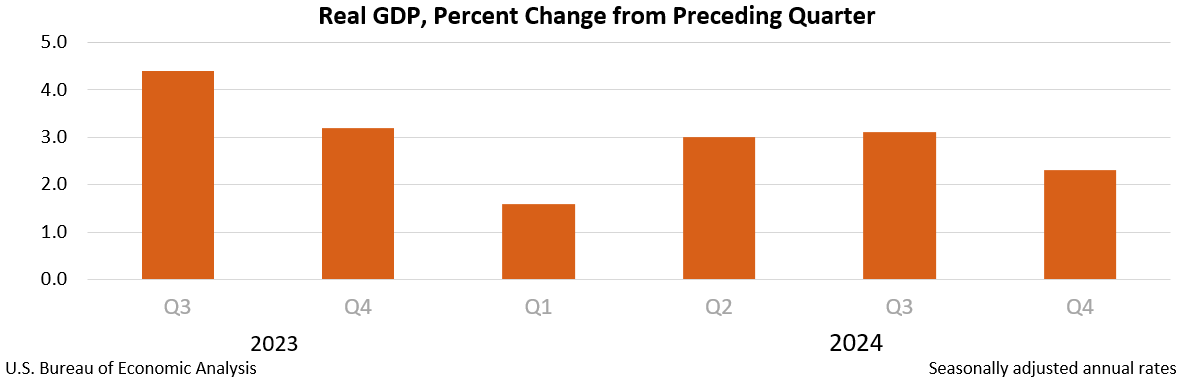
Real gross domestic product (GDP) increased at an annual rate of 2.3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2024 (October, November, and December), according to the advance estimate released by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the third quarter, real GDP increased 3.1 percent.
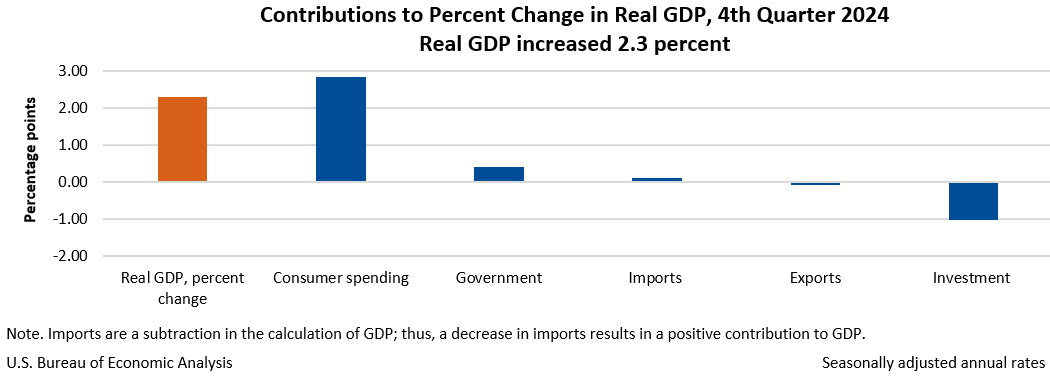
The increase in real GDP in the fourth quarter primarily reflected increases in consumer spending and government spending that were partly offset by a decrease in investment. Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP, decreased. For more information, refer to the “Technical Notes” below.
Compared to the third quarter, the deceleration in real GDP in the fourth quarter primarily reflected downturns in investment and exports. Imports turned down.
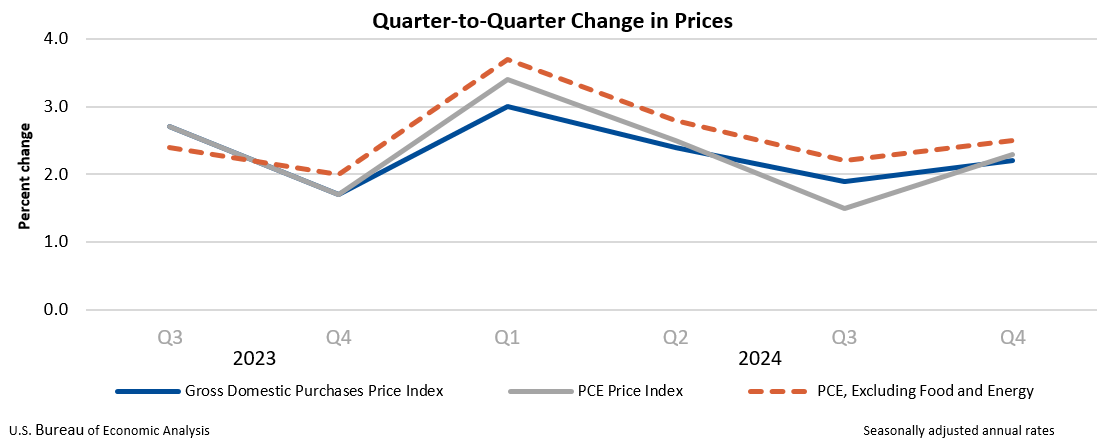
The price index for gross domestic purchases increased 2.2 percent in the fourth quarter, compared with an increase of 1.9 percent in the third quarter. The personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index increased 2.3 percent, compared with an increase of 1.5 percent. Excluding food and energy prices, the PCE price index increased 2.5 percent, compared with an increase of 2.2 percent.
| Real GDP and Related Measures | |
|---|---|
| (Percent change from preceding quarter) | |
| Real GDP | 2.3 |
| Current-dollar GDP | 4.5 |
| Gross domestic purchases price index | 2.2 |
| PCE price index | 2.3 |
| PCE price index excluding food and energy | 2.5 |
GDP for 2024
Real GDP increased 2.8 percent in 2024 (from the 2023 annual level to the 2024 annual level), compared with an increase of 2.9 percent in 2023. The increase in real GDP in 2024 reflected increases in consumer spending, investment, government spending, and exports. Imports increased.
The price index for gross domestic purchases increased 2.3 percent in 2024, compared with an increase of 3.3 percent in 2023. The PCE price index increased 2.5 percent, compared with an increase of 3.8 percent. Excluding food and energy prices, the PCE price index increased 2.8 percent, compared with an increase of 4.1 percent.
Next release: February 27, 2025, at 8:30 a.m. EST
Gross Domestic Product, 4th Quarter and Year 2024 (Second Estimate)
Technical Notes
Sources of change for real GDP
Real GDP increased at an annual rate of 2.3 percent (0.6 percent at a quarterly rate1), primarily reflecting increases in both consumer and government spending. Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP, decreased.
- The increase in consumer spending reflected increases in both services and goods. Within services, the leading contributor to the increase was health care. Within goods, the leading contributors to the increase were recreational goods and vehicles as well as motor vehicles and parts.
- Within health care, hospital and nursing home services (notably hospital services) and outpatient services increased, based primarily on Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Current Employment Statistics (CES) employment, earnings, and hours data.
- The increase in recreational goods and vehicles was led by information processing equipment, based on Census Bureau Monthly Retail Trade Survey data.
- The increase in motor vehicles and parts was led by new light trucks, based primarily on unit sales data from Wards Intelligence.
- The increase in government spending reflected increases in state and local as well as federal government spending.
- Within state and local government spending, the increase was led by compensation of employees, based primarily on employment data from the BLS CES.
- Within federal government spending, the increase was led by defense consumption expenditures, based primarily on Monthly Treasury Statement data.
More information on the source data and BEA assumptions that underlie the fourth-quarter estimate is shown in the key source data and assumptions table.
Impact of Hurricane Milton on fourth-quarter 2024 estimates
Hurricane Milton made landfall as a Category 3 hurricane just south of Tampa Bay, Florida, on October 9, 2024, bringing damage from high winds, including significant tornado activity, and extensive inland flooding.
This disaster disrupted usual consumer and business activities and prompted emergency services and remediation activities. The responses to this disaster are included, but not separately identified, in the source data that BEA uses to prepare the estimates of GDP; consequently, it is not possible to estimate the overall impact of Hurricane Milton on fourth-quarter GDP. The destruction of fixed assets, such as residential and nonresidential structures, does not directly affect GDP or personal income. BEA estimates of disaster losses are presented in NIPA table 5.1, “Saving and Investment.” BEA's preliminary estimates show that Hurricane Milton resulted in losses of $27.0 billion in privately owned fixed assets ($108.0 billion at an annual rate) and $3.0 billion in state and local government-owned fixed assets ($12.0 billion at an annual rate).
For additional information, refer to "How are the measures of production and income in the national accounts affected by a disaster?” and "How are the fixed assets accounts (FAAs) and consumption of fixed capital (CFC) impacted by disasters?”
1. Percent changes in quarterly seasonally adjusted series are displayed at annual rates, unless otherwise specified. For more information, refer to the FAQ Why does BEA publish percent changes in quarterly series at annual rates?.